 CONSERVATION PIECE: AN ABACO ECO-MISCELLANY
CONSERVATION PIECE: AN ABACO ECO-MISCELLANY
From time to time I post individual items on the CONSERVATION page. This comprises an assortment of articles, photos, videos and graphics with an eco-message relevant to Abaco and its waters. They accumulate gradually, and occasionally it is good to post a selection for consideration. What is the most frequently found item of detritus on a beach? Is it ok to eat striped bass? How many uses does a coconut have? How quickly does the invasive lionfish population spread? What is Fish Pharm? How many years does it take for an aluminium can to decompose? These and many other questions are answered below.
 Click logo for website!
Click logo for website!
NOAA MARINE DEBRIS PROGRAM
ICC volunteers clean 10 million lbs of trash from our coasts
May 16, 2013 by NOAA Marine Debris Program
One rubber chicken, 117 mattresses, 4,159 candles, and 689,274 utensils. What do all of these things have in common?
They’re all marine debris collected last September at the Ocean Conservancy’s 2012 International Coastal Cleanup®, sponsored in part by the NOAA Marine Debris Program.The numbers are in: more than 550,000 volunteers came together to collect 10 million pounds of marine debris. In the United States, volunteers found enough bottles that, when stacked end to end, equal the height of 1,000 Empire State Buildings. That’s a lot of trash on our beaches and in our waterways!This litter is threatening our marine environment, economy, and health, and the problem will only get worse unless we change the way we consume and dispose of products. There are solutions, and we can prevent litter from ending up in the ocean.So here’s a challenge: the next time you use a throw-away item: a bag, bottle, or utensil, answer the question, “Where it’s going?” How will you keep your items from becoming litter in our oceans, rivers, and streams? Head to Ocean Conservancy’s data release page for some neat infographics on last year’s trash haul. Here are the top 10 types volunteers found this year

THE PELAGIC OCEAN: AN INVESTIGATION INTO POLLUTION – BY KIDS
Prepare to be astounded – and horrified – by the cruel damage inflicted on sea life by humans and their prolific plastic trash. Credit: Friends of the Environment, Abaco

PROPOSED MARINE PROTECTED AREAS / EAST ABACO CREEKS VIDEO
BAHAMAS LIGHTHOUSE PRESERVATION SOCIETY

LIONFISH

The debate about the seemingly unstoppable spread of the invasive lionfish species is well known. There are some who argue strongly that lionfish have their uses, and not merely as a food source. To see ongoing lionfish research by the organisation REEF click HERE To supplement the static projection graphic for lionfish spread (below), here is an active graphic that vividly shows how the species (love them or hate them) has expanded exponentially in numbers and range over a very short period








 National Geographic
National Geographic

LOBSTERS – WE GOTTEM! OVERFISH THEM – WE AIN’T!
Video courtesy the fabulous CONCH SALAD TV; heads-up from ABACO SCIENTIST; campaign by SIZE MATTERS

BAHAMAS LIGHTHOUSE PRESERVATION SOCIETY Read the Society’s 4-page January 2013 Newsletter HERE BLPS NEWSLETTER JAN 2013
The Society was founded in 1995, and it has already achieved much to preserve and protect the lighthouses of the Bahamas. Of particular interest to Abaconians will be the news about the Hope Town lighthouse, and about the work done at Hole-in-the-Wall. If you’d like to support this hard-working not-for-profit organisation and help to preserve a part of Abaco’s maritime history, the email address is blps.bah@gmail.com 

A new environmental organisation has been announced: to find out more
CLICK===>>> BPFA





IUCN CUBAN PARROT RED LIST RANGE MAP FOR AT RISK SPECIES
I have annotated this IUCN map of the Cuban Parrot population range. It’s worth noting that the Bahamian subspecies is now found only as a breeding population on Abaco and Inagua, being defunct on all other islands since the mid-c20. Of these populations, only the Abaco parrot breeds underground, a unique feature among the whole species.
I am puzzled by the suggestion of an ‘extant (resident)’ population on the Bimini Is. That would suggest that they breed there. I don’t know the date of the map, but I have checked with the Avibase bird database, and the Cuban parrot is indeed included in the list of Bimini birds. I’ve put a query on the map because I don’t know what the position is in 2012.
Click me!
FRIENDS OF THE ENVIRONMENT (ABACO)
This conservation organisation has recently completely redesigned its website (click logo above), and presents comprehensive and easily navigated information about a myriad aspects of conservation on Abaco and its fragile ecology. The fragility is mostly directly or indirectly caused by mankind (a broad statement, I know, but it’s an arguable stance), so it’s worth checking out the measures that are being undertaken to preserve the natural resources of the island and its cays. Below is a post about one feature highlighted on the FotE site that I am particularly interested in. Overall all the new website is definitely one for any Abaconian (or, like me, regular visitor) to study. If you want to contribute your support (either generally or to a specific cause) go to the FotE website (click logo) or visit the Rolling Harbour wildlife charity page
HERE
THE EFFECT OF RISING SEA LEVELS IN THE CARIBBEAN
This map has been posted by the SCSCB, with the very interesting and definitely worrying text “The map shows projected impacts of a 2 meter sea level rise in the Caribbean. The orange is the impact of 2 meters, while the yellow is the 25 meter line. The last time the ice caps melted the sea rose between 18 and 25 meters. The most conservative estimates indicate a 1-meter rise by the end of the century (concurrent with a 2 degree C rise in temperature). From the position of planning, I am curious about the estimates being used by Caribbean resource managers in their long-range planning. For example, what percentage of Caribbean seabirds nest below 2 meters…”

EAST ABACO CREEKS NATIONAL PARK PROPOSAL
Click on the title above to see the BNT’s proposal for this major conservation proposal for the east Abaco creeks. It’s in .pdf form and you can (probably) copy / save it if you wish. The map below shows the 3 areas concerned. You can check out more details – and photos – on Facebook at EACNP


A VISUAL TO PONDER FROM ‘SCIENCE IS AWESOME’




CONSERVATION ON ABACO AND IN THE BAHAMAS
This new page (June 2012) is intended to showcase the achievements of the various organisations and individuals involved with the protection and conservation of the fragile ecology and wildlife in a small and rapidly developing area. A number of posts and articles from other pages will gradually migrate to this page.
I have posted on Facebook a statement by the new Environment Minister which praises the environmental work carried out in the Bahamas and pledges Government support MINISTER’S STATEMENT Let’s hope it’s forthcoming…

CONCH CONSERVATION
The supply of conchs is not infinite. Overfish them, take them before maturity or pollute their habitat and this valuable marine resource depletes – and conchs, as with so many marine species, will become threatened. Fortunately there is a Bahamas-wide conservation organisation with a website packed with interest. COMMUNITY CONCH is “a nonprofit organization that aims to protect queen conchs in the Bahamas, a species of mollusk threatened by aggressive over-fishing. We promote sustainable harvest of queen conch through research, education and community-based conservation”
“Helping to sustain a way of life in the Bahamas”
Much of the research has been carried out in Berry Is, Andros and Exuma Cays. However the team has recently been based at Sandy point, Abaco CLICK===>>> ABACO EXPEDITION The full Conch Conservation post can be found at CONCH QUEST

BAHAMAS MARINE MAMMAL RESEARCH ORGANISATION (BMMRO)
The BMMRO is featured many times in this blog, in particular in the pages WHALES & DOLPHINS and MANATEES. They now have a Facebook page with all the latest news, photos, newsletters links and cetacean / sirenian goss in one easily-digested timelined place. To reach it CLICK ===>>> BMMRO FACEBOOK PAGE
For the latest quarterly newsletter, just published, CLICK ===>>> BMMRO NEWSLETTER JULY 2012


A RECENT FLYER FOR THE ‘SIZE MATTERS’ CRAWFISH CAMPAIGN

BAHAMAS NATIONAL TRUST PRESS RELEASE JUNE 2012
ABACO PARROT POPULATION ON THE RISE
 The Bahamas National Trust in conjunction with Dr. Frank Riviera and Caroline Stahala recently conducted an intensive survey of the Bahama Parrot on Abaco Population surveys conducted in 2002 resulted in estimates of the Abaco parrot population of about 2,500 parrots with similar values in the following years. This year Dr. Frank Rivera and Caroline Stahala, who took part in the initial surveys, helped by BNT wardens and volunteers, conducted a 10 year follow up survey to determine the change in the Abaco parrot population since management began. The results indicate that the Abaco parrot population has increased since the BNT’s management efforts were implemented with a new estimate of just over 4,000 parrots on Abaco. The BNT has been concerned about the Bahama Parrot Population since the 1980’s. Studies indicated that the major threat to the parrots were feral cats who cause serious problems to the parrots during the nesting season by entering the underground nesting cavities and killing the breeding adults and chicks. The BNT implemented an intensive predator control effort in 2009 throughout the parrot nesting area culminating in the hiring of Marcus Davis as Deputy Park whose primary responsibility is to oversee the predator control program. During the breeding seasons the BNT has seen a decrease in the number of breeding parrots killed and nest success increase. The question, though, remained whether this effort would translate into an increase in the Abaco parrot population size. Survey results indicated that predator control has led to an increase in nest success. In addition, the Abaco parrots have weathered several hurricanes (Frances, Jean and Irene) over the last 10 years and still appear to show a population increase. Hopefully with continued management efforts a healthy and viable endemic parrot population on Abaco will continue to thrive. According to David Knowles, BNT Director of Parks “This gives us hope that with continued management efforts we can continue to have a healthy and viable endemic parrot population on Abaco.”
The Bahamas National Trust in conjunction with Dr. Frank Riviera and Caroline Stahala recently conducted an intensive survey of the Bahama Parrot on Abaco Population surveys conducted in 2002 resulted in estimates of the Abaco parrot population of about 2,500 parrots with similar values in the following years. This year Dr. Frank Rivera and Caroline Stahala, who took part in the initial surveys, helped by BNT wardens and volunteers, conducted a 10 year follow up survey to determine the change in the Abaco parrot population since management began. The results indicate that the Abaco parrot population has increased since the BNT’s management efforts were implemented with a new estimate of just over 4,000 parrots on Abaco. The BNT has been concerned about the Bahama Parrot Population since the 1980’s. Studies indicated that the major threat to the parrots were feral cats who cause serious problems to the parrots during the nesting season by entering the underground nesting cavities and killing the breeding adults and chicks. The BNT implemented an intensive predator control effort in 2009 throughout the parrot nesting area culminating in the hiring of Marcus Davis as Deputy Park whose primary responsibility is to oversee the predator control program. During the breeding seasons the BNT has seen a decrease in the number of breeding parrots killed and nest success increase. The question, though, remained whether this effort would translate into an increase in the Abaco parrot population size. Survey results indicated that predator control has led to an increase in nest success. In addition, the Abaco parrots have weathered several hurricanes (Frances, Jean and Irene) over the last 10 years and still appear to show a population increase. Hopefully with continued management efforts a healthy and viable endemic parrot population on Abaco will continue to thrive. According to David Knowles, BNT Director of Parks “This gives us hope that with continued management efforts we can continue to have a healthy and viable endemic parrot population on Abaco.”
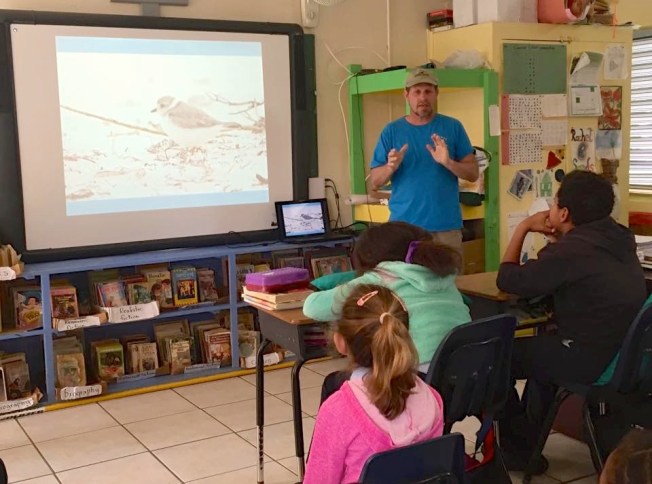
















































































 (A quick shout-out to Tom Reed, who I know took the piping plover photo!)
(A quick shout-out to Tom Reed, who I know took the piping plover photo!)


















































































































 National Geographic
National Geographic




















You must be logged in to post a comment.