“THE DIET OF WORMS”: WORM-EATING WARBLERS ON ABACO
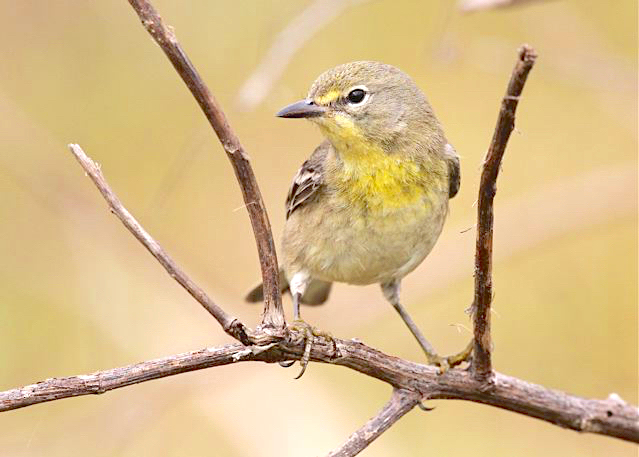
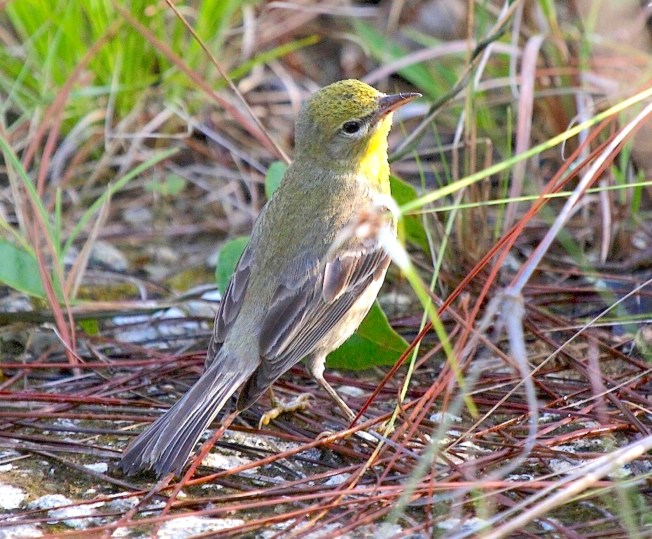
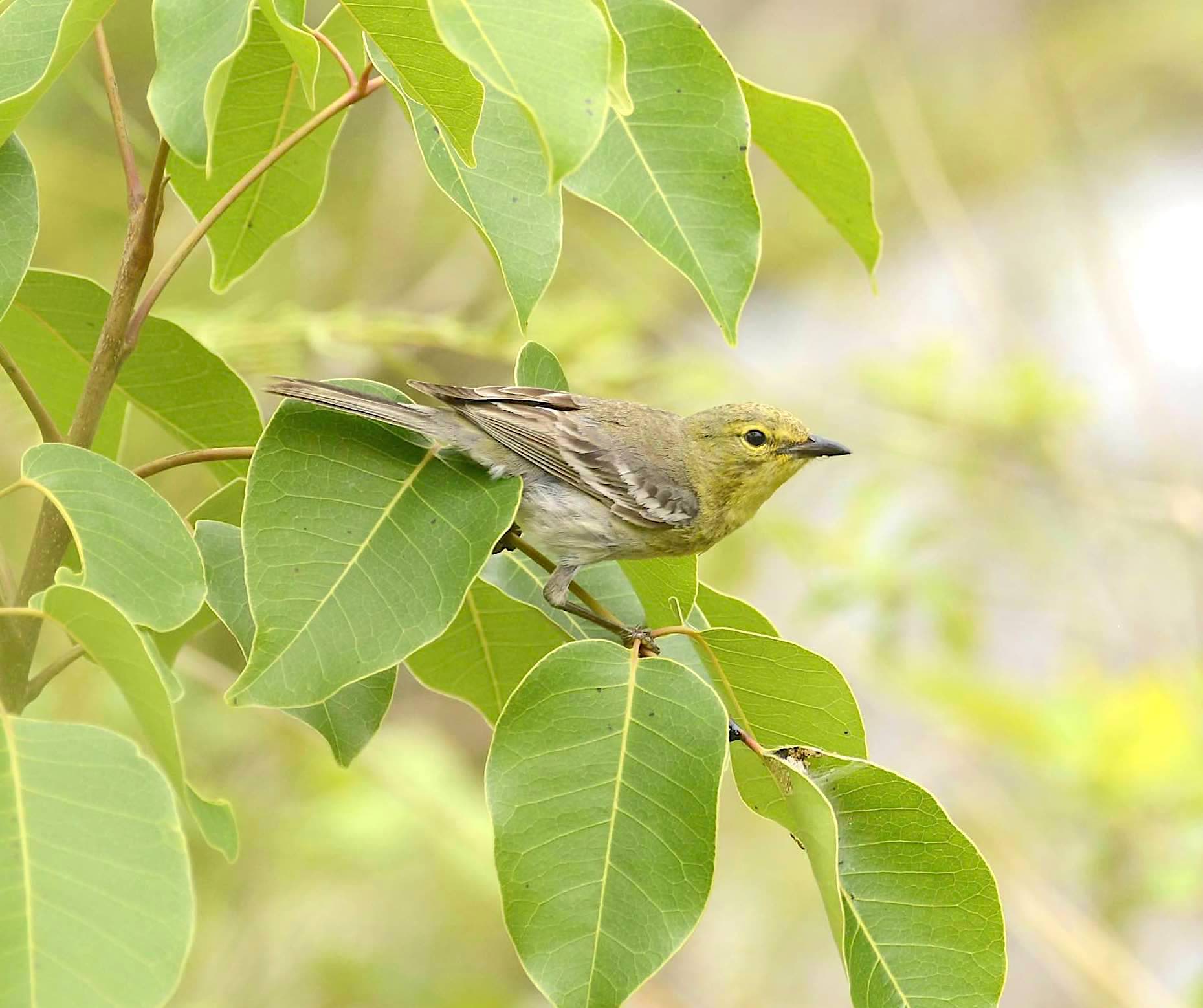
The little worm-eating warbler (Helmitheros vermivorum) is unique. Not because of its worm-eating propensities or its warbler-ishness (or the combination), but because it is the only species currently classified in the genus Helmitheros. The Swainson’s warbler was once in the same genus, but the WEWA saw off the competition.
SO WHAT IS A HELMITHEROS THEN, IF IT’S SO SPECIAL?
The word is Greek, meaning something like ‘grub-hunter’. And the Latin-derived vermivorum reflects the diet of a VERMIVORE – an eater of worms. But this description is, like a worm, somewhat elastic. It includes caterpillars, larvae, grubs, spiders and similar creatures. But whereas there are other warbler vermivores there is only one Helmitheros.
SOME WORM-EATING FACTS TO DIGEST
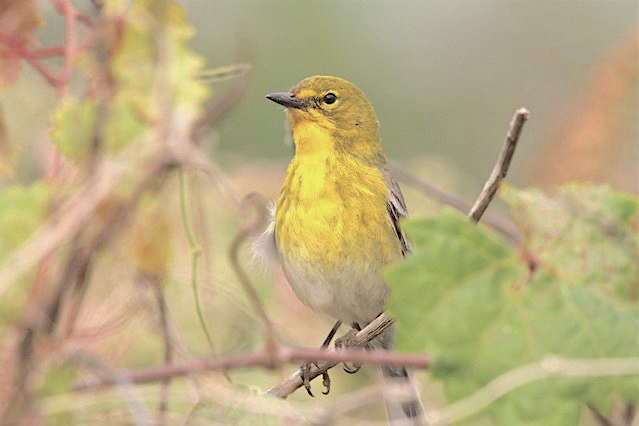
- WEWAs are sexually monomorphic. Males & females are indistinguishable for most of the year
- They can only be reliably sexed at the height of the breeding season…
- …don’t ask. OK, a magnifying glass may be needed
- They are believed to eat actual earthworms quite rarely. Moth larvae are their best treat
- They are ground-nesting birds, one of only 5 new-world warblers to do this
- Like some shore-birds, adults may feign injury to lure predators away from the nest
- They are vulnerable to nest parasitism by brown-headed cowbirds & feral cats
- Fires, deforestation, habitat change & diminished food resources are all threats to the species
- As are pesticides, which destroy the primary food source and are in any case potentially toxic
DISTRIBUTION & CONSERVATION STATUS
The breeding range of the worm-eating warbler covers much of the eastern half of the US as far south as the Gulf Coast. It winters in the West Indies, Central America and southeastern Mexico. There is no overlap between summer and winter habitat. Because of the vulnerability of this ground-nesting species to a number of threats (see FACTS above), they are now IUCN listed as ‘Special Concern’ in New Jersey.
WHAT DO THEY SOUND LIKE?
In this case the song and call, as transposed into human, really does sound like the bird itself. The song is a rapid squeaky trill; and the calls for once do actually sound like ‘chip’ or ‘tseet’. See what you think (turn up the volume a bit).
Paul Marvin / Xeno-Canto
THE (ORIGINAL) DIET OF WORMS – A DIGRESSION
Studied European history? Had a laugh over The Diet of Worms in 1521? This was an assembly (or ‘Diet’) of the Holy Roman Empire that took place in the City of Worms in Germany. There had already been several of them. This one resulted in an edict concerning Martin Luther and protestant reformation, with the consequence that… [sorry, I’ll spare you the details. I’ve started yawning already, just as I did at school I expect]
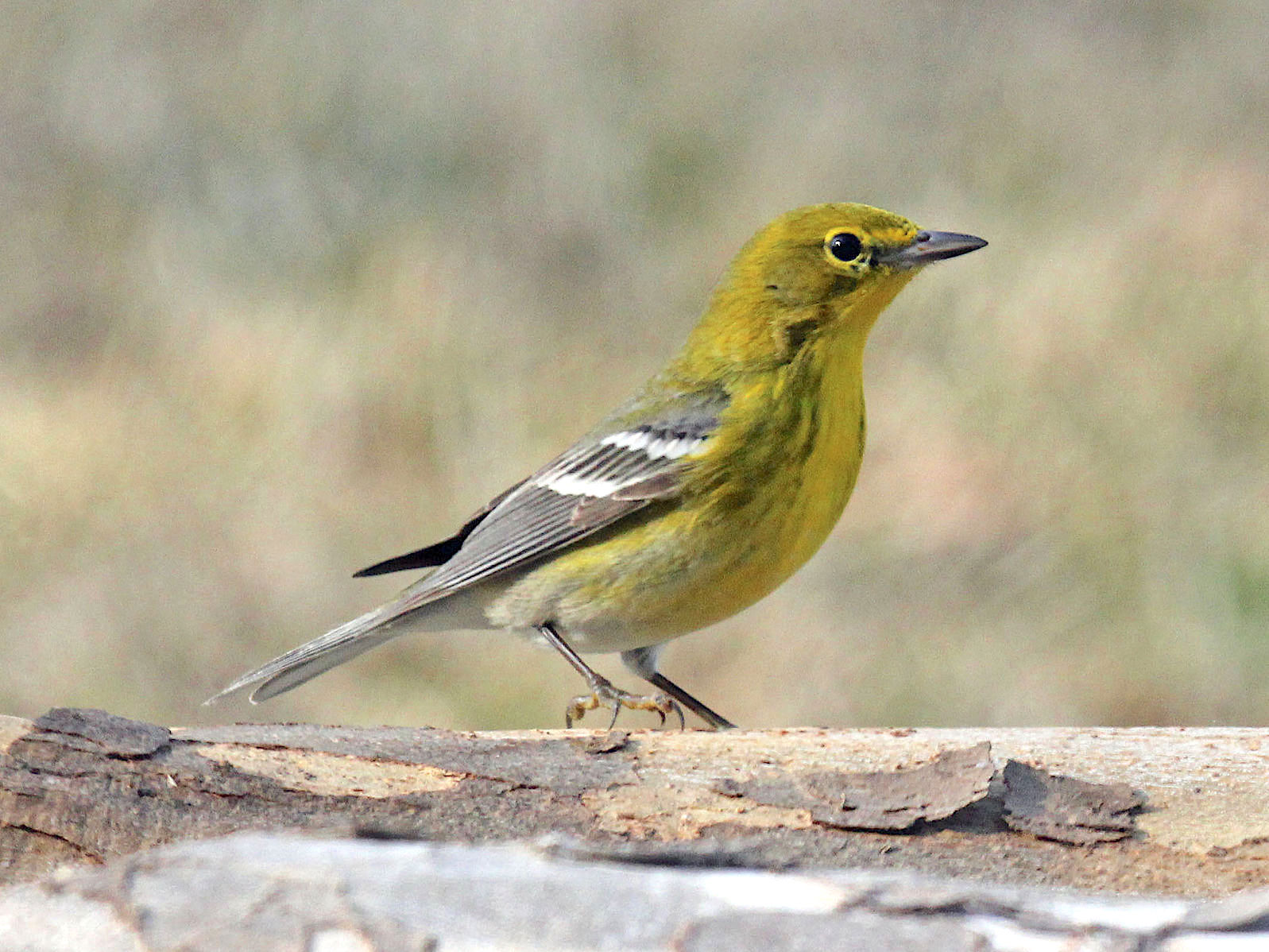
It is always instructive to look at Audubon’s fine depictions from the early c19. Here is his WEWA. Notice that it is here called Sylvia vermivora. So he had the worm-eating part, but the first part of the name – referencing woods – rather strangely relates to a group of old-world warblers. No, I’ve no idea why.
Credits: Photos – Tom Sheley (1); Charmaine Albury (2, 4, 6); Andy Reago & Chrissy McClarren (3, 7); Tom Friedel (5). Research material – CWFNJ / Michael J Davenport; Tom Fegely / The Morning Call; assorted magpie pickings & open source






























































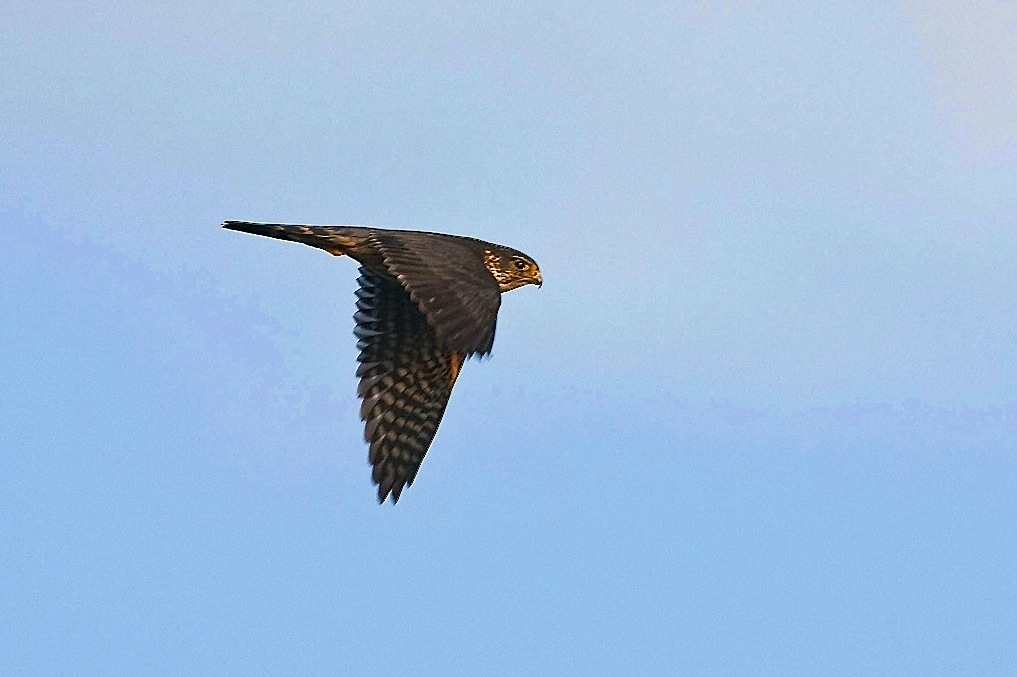
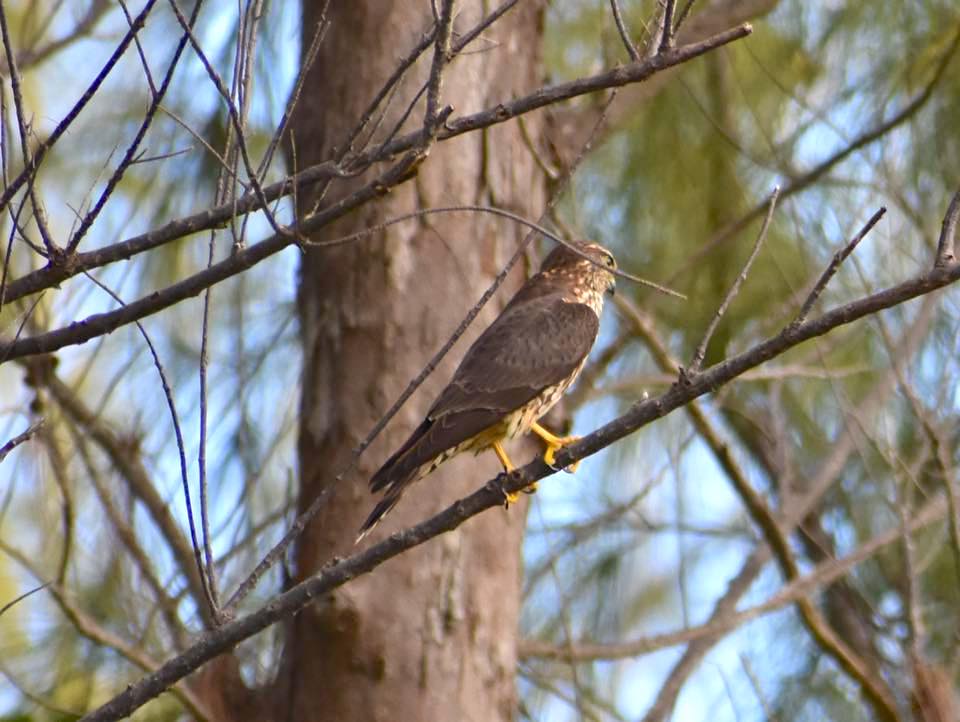
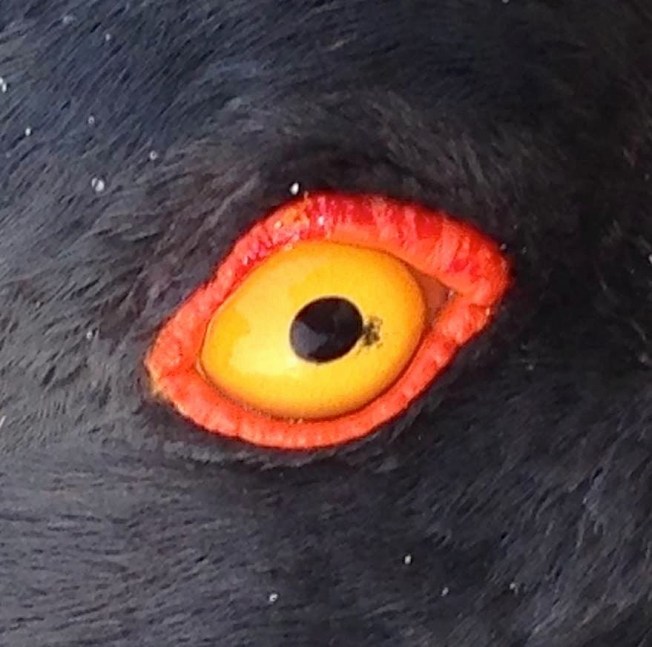
 FIERCE LITTLE FALCONS: MERLINS ON ABACO
FIERCE LITTLE FALCONS: MERLINS ON ABACO





























































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.