‘A SADNESS OF SHEARWATERS’ ON ABACO
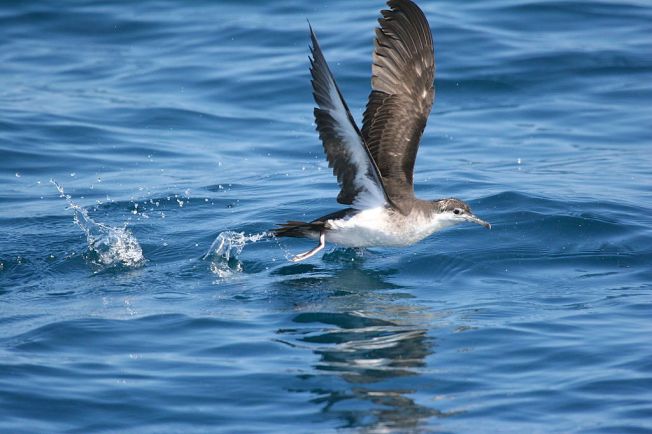
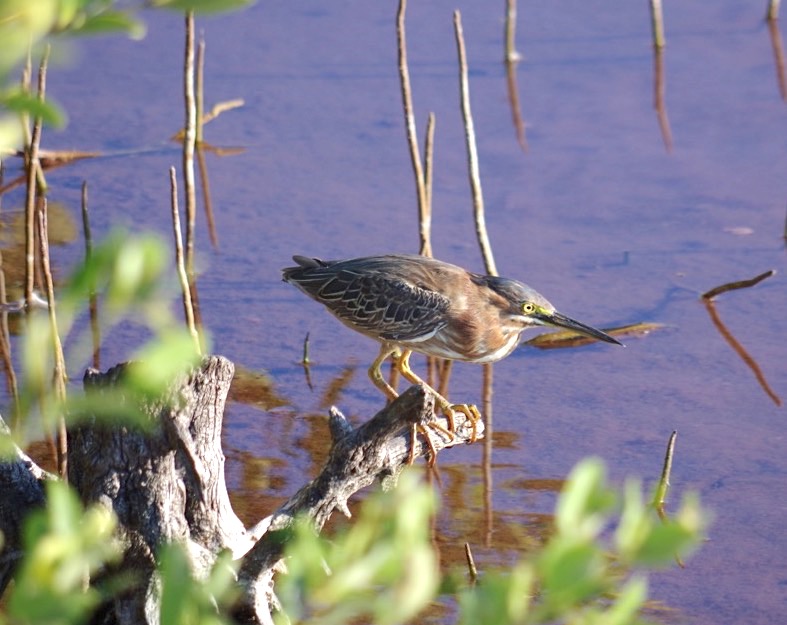
If you are walking your favourite beach on Abaco right now, it’s quite possible you may see – or may already have seen – a very poorly seabird. Or one that is dead, I’m afraid. These are Audubon’s Shearwaters, also known as Dusky Petrels. They are the only permanent resident shearwater species on Abaco. Three others (Cory’s, Great and Sooty) are rare transients; and the last – the Manx – is a very rare off-course vagrant.
Each sad bird is part of a tragic and recurrent phenomenon, a so-called die-off event. As in previous years, a few of the birds that succumb may be Great Shearwaters mixed in with the Audubon’s. I first became aware of this problem in June 2015 and wrote two detailed posts about the situation. This bleak time lasted for about a week, and many reports came in from the mainland and the cays from Green Turtle Cay right down to Crossing Rocks, all duly mapped to get the overall picture.
There was thankfully no such problem in 2016, but in 2017 – also in June – there was another die-back event involving a large number of Audubon’s shearwaters (Puffinus lherminieri) appearing in the tideline and on beaches. Many were already dead. Some are still alive, but in a very poor state. The prospects for recovery for birds that were captured and cared for were not good.
Two years on, and the melancholy cycle is repeating itself. A few days ago, Melissa Maura, an expert in the care and recovery of creatures of all kinds, posted an alert and some sound advice:
A heads-up to all Island folk that it appears to be a summer when exhausted Shearwaters (pelagic seabirds) are washing up on our beaches in Eleuthera and Abaco. I have had two calls in 24 hours. Should you find one, understand that it will be in a severe state of exhaustion and stress and that excessive handling will kill it. Please put in a safe pen on a sandy surface, with shallow pan of fresh water and try locate either fresh fish (important) or squid from a bait shop. This may have to be administered by gently opening the beak and inserting one inch long piece of fish every couple of hours until stable. Ideally they need tube feeding, but very few folk can do this. Please contact me on private message if you find any…
An exhausted Audubon’s Shearwater, now being cared for by Melissa Maura








































































 Credits: Dan Stonko / American Bird Conservancy, Michael Baltz / Bahama Oriole Project / Kevin Omland; Mary Kay Beach; Bahama Oriole Project FB header; C Ward / BNT; Thomas Nierle / Bahama Oriole Project; Bahamas Postal Service; BNT; D Belasco / American Bird Conservancy; Handbook of World Birds (drawing)
Credits: Dan Stonko / American Bird Conservancy, Michael Baltz / Bahama Oriole Project / Kevin Omland; Mary Kay Beach; Bahama Oriole Project FB header; C Ward / BNT; Thomas Nierle / Bahama Oriole Project; Bahamas Postal Service; BNT; D Belasco / American Bird Conservancy; Handbook of World Birds (drawing)






















































































You must be logged in to post a comment.