
 Click logo for website
Click logo for website

3 MONTHS ON ABACO WITH THE BMMRO: AN INTERN’S STORY
My name is Jack Lucas and I am Marine Biology Student at Plymouth University in the UK. I came to the Bahamas Marine Mammal Research Organisation on Abaco in July 2013 for a 3 month internship, which has been an amazing experience from start to finish. Heres a summary of my summer spent at BMMRO.
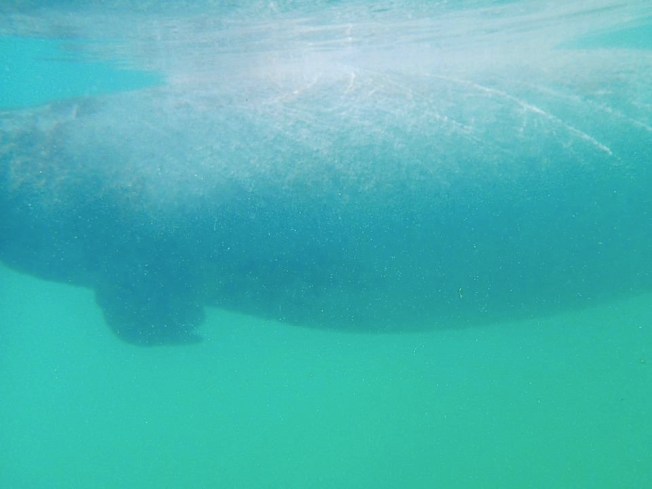
Sperm Whale Fluking
I arrived at the start of July and was fortunate enough with my timing to be part of an assembled crew of scientists from all over the world coming together to start work on what was to be this summers main project; collecting faecal samples from Blainville’s beaked whales to assess stress hormones produced. This team included Dr Roz Rolland and Dr Scott Kraus from New England Aquarium, who are collaborating with BMMRO for the work, and the samples will be analysed back at their lab in the US. Also along for the ride was Roxy Corbett; a whale observer and field researcher from the US, and Dr Stephanie King; a acoustician from the Sea Mammal Research Unit in Scotland. The first day after arriving it was straight out on the boat to search for these elusive creatures and the beginning of a crash course in how to collect and store the faecal samples when we found them. For the first week the work was a mix of boat work when the weather permitted and practicing poop collection using custom-made fine-mesh nets and coffee grounds (as close to the real thing as we were willing to try!), as well as clearing out BMMRO’s garage and, under the direction of foreman Scott, the construction from scratch of a lab to prepare samples for storage.
An example of the use of coffee grounds to practise whale poop-scoop technique RH note: NOT Jack’s arms / snappy diving suit…
RH note: NOT Jack’s arms / snappy diving suit…
Unfortunately, despite days of poop collection practice and endless hours searching for the whales at sea, the original poop team never got a chance to employ these by now highly developed skills or to see the lab being used, as the weather was so windy we barely encountered the animals let alone spent long enough with them to collect any samples.
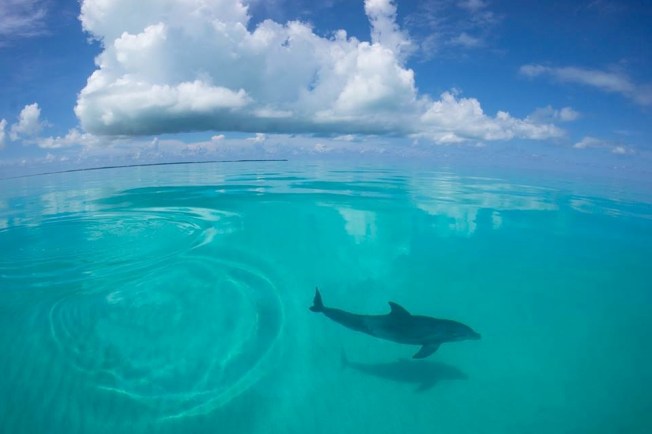
Despite the lack of beaked whales, we did encounter loads of marine mammals in the first few weeks, from sperm whales to three different species of dolphin; including the little-seen and even less-studied rough-toothed dolphin.
Rough-toothed Dolphin
After discussion with Charlotte and Di about a possible project for me to complete during my stay, it was to be this species that I would focus on and in between the usual office jobs it was my task to sort through the photos from 20 rough toothed encounters in the Bahamas since 1995 and create a catalogue of individuals. This initial task consisted of careful inspection, comparison and sorting of what turned out to be over 5000 photos, into an organised catalogue of 167 separate and distinctive individuals. Despite the hours of endless staring at fins, it was very rewarding as there were 13 resighted individuals found (we were not necessarily expecting any!) which suggests long-term site fidelity and association of these animals, in addition to year round use of the Grand Bahama Canyon. Even more rewarding; the results of this work have recently been submitted for a poster display at an Odontocete workshop in New Zealand this December and I am also writing up the results in a formal scientific paper, with the hopeful goal of publishing a note in a peer-review journal.
Scott, Jack, Stephanie and Di in the new lab at Sandy Point
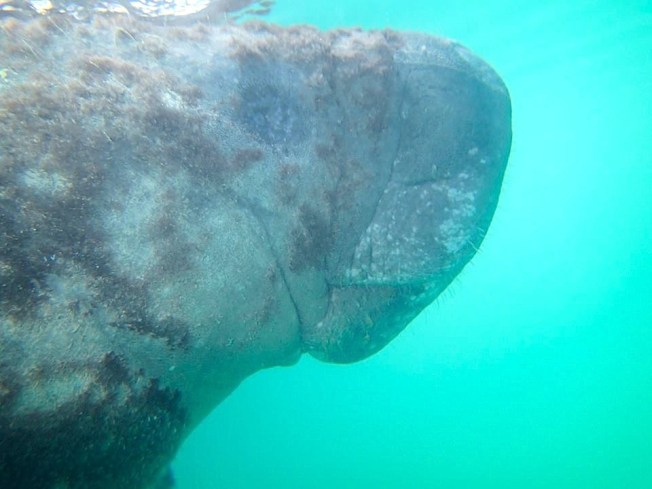
Around a month in I was lucky enough to be sent by Di and Charlotte to Great Harbour Cay on the nearby Berry Islands to work with the manatees there, in particular Georgie; a recently released juvenile whose status is being carefully monitored after her rehabilitation at Atlantis’ Dolphin Cay following health problems. The work here for a week under the guidance of Kendria; a Bahamian contracted by BMMRO to monitor the manatees on the Berry Islands, consisted of tracking Georgie using a satellite tag attached to a belt around her tail. Once located, we logged her position and made any notes on her health and behaviour aswell as the other manatees that were often found with her (there are currently 6 located on Great Harbour Cay). Two days in her tag was found unattached at a locals dock (it has a weak-link incase of entanglement) and we had to locate her using underwater hydrophones to detect her belt. Once found, I had the rare opportunity of entering the water with her in order to re-attach a new tag to her belt; it was amazing and one of the best encounters I have had with any animal! It is impossible not to love these amiable and gentle creatures, especially when you observe their infamous ‘hugs’ in person!
Georgie the Manatee
For more about Georgie’s re-release in the Berry Is. after her earlier shenanigans on Abaco, see HERE
After returning from the Berry Islands (and incidentally missing the first two poop collections of the season made by Charlotte!) it was back to hunting for the elusive beaked whales around South Abaco. During my time I had the chance to work with several interns coming to BMMRO including local marine-enthusiasts Tristan and AJ, and Courtney Cox from Florida. Oscar Ward from the UK also joined the team as Charlotte left for Scotland to complete her PhD, and was on hand during the poop-collection and other little excursions. In wasn’t until the last month of my time here that we managed to get close enough to the whales for me to get in the water and be towed alongside in the hope of seeing one defecate. One amazing morning two whales surfaced right off the bow of the boat and what resulted was again, one of the most amazing moments; swimming just a couple of feet away from an animal only a handful of people in the world have seen underwater. After nearly two months with no samples, the two weeks that followed were a flurry of boat days, poop-collection and whale watching; with a total of 7 samples collecting from beaked whales (5 in one day!!) and another 3 from sperm whales. This was the best possible end to my time here and I finally got a chance to use the much-practiced poop collection techniques. The samples included a number of squid beaks, and in one very deep dive collection a mass of parasitic worms and a weird cephalopod-type animal! We also got a chance in the last few weeks to test-run a new addition to the fleet, that included a dive compressor.
Ready to collect some poop…
Finally my time in the Bahamas had to come to an end, and I had to return home. The last 3 months has flown by and has been one of the most enjoyable and most importantly educational periods of my life and I cannot thank Di and Charlotte enough for making it all possible. The day-to-day boat runs, office work, equipment maintenance and station chores has given me a good insight into all aspects of field research. It was my first taste of life as a marine mammal scientist, and it has made me even more determined to pursue a career in this field; a perfect stepping stone from which to move forward. In addition my work with BMMRO (and what must of been a brilliant reference from the girls!) made it possible to secure a highly competitive internship in the Farallon Islands this winter tagging elephant seals amongst other work! I cannot wait to continue working in this field and finish writing up the results of my project here, and hope I have the chance to come to Abaco again to work with these amazing people and animals!
BMMRO would like to thank Jack for all his help during the summer, and all our interns for their assistance! To our sponsors, Friends of the Environment, Disney Animal Programs and Environmental Initiatives and Rotary of Abaco, we thank you for your continued support.
To read more about the work of Interns on Abaco with the BMMRO at Sandy Point and Friends of the Environment in Marsh Harbour, check out Oscar Ward’s excellent blog SEVENTYPERCENTBLUE. There are articles on Life in the Mangroves, the Bahamas Climate, Whale Poop Collection, and most intriguing how he and co-intern Jack both came very close to being Black Tip Fodder… real live Chums!
The Author researching underwater creatures





































































![ShawnCarey[3]](https://rollingharbour.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/shawncarey3.jpg?w=300&h=210)











































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.