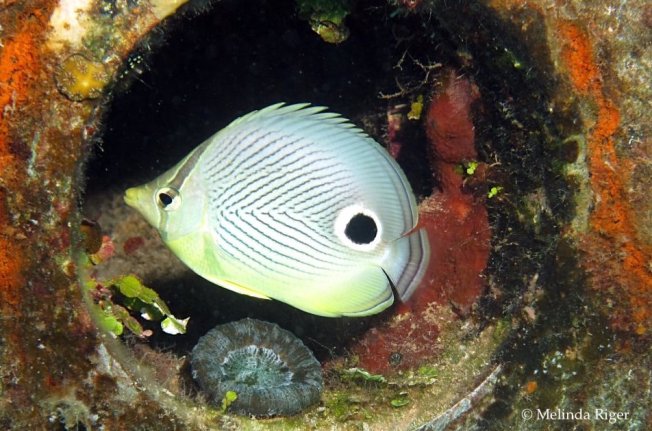
BAHAMAS REEF FISH (44): PORKFISH
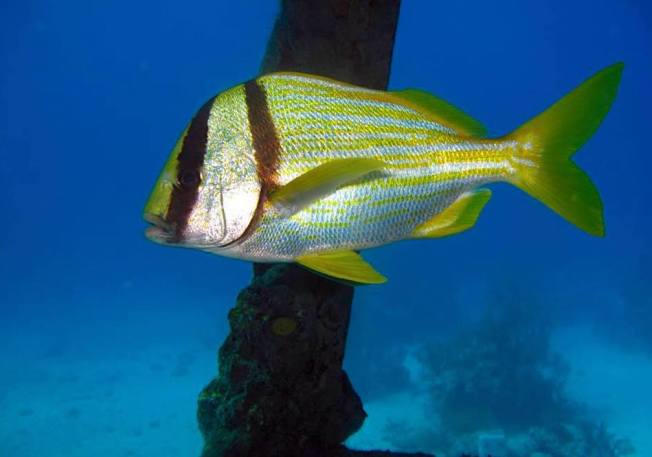
Behold the porkfish Anisotremus virginicus, the slightly unattractively named representative of the (arguably) even less attractively named grunt species. These small, bright-coloured reef dwellers are rarely more than 12 inches long. They are mainly nocturnal fish, feeding on small crustaceans, mollusks and so on. Juveniles have been observed acting as cleaners to larger species, feeding on parasites – an example of mutualism between species, in which both sides benefit from the arrangement.
WHY IS A ‘PORKFISH’ A ‘GRUNT’
The terminology seems to be somewhat confused by local usages, but in general terms all porkfish are grunts; but not vice versa. Yet I notice that the term ‘porkfish’ is used to describe other types of grunt. A good rule of thumb is the the Atlantic Porkfish is the only grunt with two black vertical bars and yellow stripes… Note that grunts differ from their cousins the snappers by having a different dental arrangement – no canine teeth.
AND WHY ‘GRUNT’ ANYWAY? DO THEY SOUND LIKE PIGS?
Well, perhaps a bit. All grunts, including porkfish, are capable of producing grunt-like sounds from some kind of grinding of their back teeth that is too technical to go into here**. The sound is associated with ‘situations of duress and danger’ – such as being caught and unhooked…
DO YOU HAPPEN TO HAVE A RECORDING?
As it so happens I do. This is taken from a rather longer Youtube video in which a grunt was caught, unhooked and returned.You’ll hear a couple of grunts as the fish was unhooked, and some (perhaps understandable) hilarity on the boat. I guess you had to be there.
Porkfish are gregarious, and also mix with other species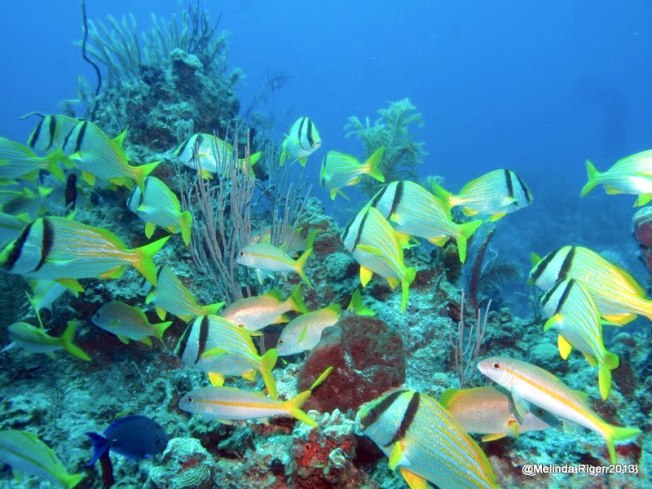
ARE PORKFISH EDIBLE?
Like most if not all grunts, they are, with the proviso that there is some association with ciguatera. I’ve never knowingly eaten one myself, but I gather that “grits and grunts” is a popular culinary combo in some places. For those that might want to know more, a quick look at a couple of threads reveals the following:
- They taste great, a bit like ham
- Their white meat cooks very well
- They taste better than black margates (another grunt species)
- Eat them in enchilado or breaded fillets
- ‘Big-ass head’ on them so not much if you filet
- If you scale and cook whole you get a better yield on them
- When fishing for supper, ‘shoot ’em up and hold off for the bigger ones’
Credits: all great photos by Melinda Riger / Grand Bahama Scuba, except the last by Brian Gratwicke (wiki); soundbite from Youtube video 2010 by peachyree; research from seaworld.org; britannica.com and the usual suspects…
** Subtle code for “I haven’t really understood it…”






































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.